Normal Heart Beat
Heart rate, also known as pulse, is the number of times a person’s heart beats per minute. A normal heart rate depends upon the individual, age, body size, heart disease, whether the person is sitting or moving, medication use and even air temperature level. Even feelings can have an impact on heart rate. For instance, getting excited or scared can increase the heart rate. But most significantly, getting fitter decreases the heart rate, by making heart muscles work more efficiently.
Understanding a Normal Heart Rate in Your Age
Normal heart sounds are associated with heart valves closing: S 1. The first heart sound, or S 1, forms the 'lub' of 'lub-dub' and is composed of components M 1 (mitral valve closure) and T 1 (tricuspid valve closure). Normally M 1 precedes T 1 slightly. It is caused by the closure of the atrioventricular valves, i.e. Tricuspid and mitral (bicuspid), at the beginning of ventricular contraction.
- At rest, a normal heart beats around 50 to 99 times a minute. Exercise, emotions, fever and some medications can cause your heart to beat faster, sometimes to well over 100 beats per minute. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
- A normal, healthy heart rate is typically between 60 and 90 beats per minute, but this can depend on your sex and ethnicity. According to a 1992 review of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, women had a slightly higher resting pulse than men.
- A normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute. Generally, a lower heart rate at rest implies more efficient heart function and better cardiovascular fitness. For example, a well-trained athlete might have a normal resting heart rate closer to 40 beats per minute.
“Your heart is a muscle and similar to enhancing other muscles by doing activities, you can do the exact same thing with your heart,” said Dr. Mary Ann Bauman, an internist at Integris Baptist Medical Center in Oklahoma City.
Understanding about your heart rate can help you monitor your physical fitness level, and it might assist you spot establishing illness if you are experiencing other symptoms.
“If you are an athlete and you’re training, or if you are having symptoms such as dizziness, then understanding your heart rate is important,” Bauman said. “However as a general guideline, unless someone is having issues, it’s not extremely important to constantly understand what your heart rate is.”
How to measure heart rate
The most convenient places to measure your heart rate are on the wrists or one side of the neck. For an accurate reading, put two fingers over one of these areas and count the variety of beats in 60 seconds. You can also do this for 20 seconds and increase by 3, which might be easier, Bauman stated. Using your thumb may be confusing since sometimes you can feel a pulse in the thumb, she said.
Resting heart rate
Your resting heart rate is your pulse when you are calmly sitting or lying. It’s best to determine your resting heart rate it in the early morning prior to you rise, according to the American Heart Association (AHA). For adults 18 and older, a typical resting heart rate is in between 60 and 100 beats per minute (bpm), depending upon the individual’s physical condition and age. For children ages 6 to 15, the normal resting heart rate is in between 70 and 100 bpm, according to the AHA.

But a heart rate lower than 60 doesn’t always mean you have a medical problem. Active people often have lower heart rates since their heart muscles do not need to work as hard to maintain a constant beat. Athletes and people who are very in shape can have resting heat rate of 40 bpm.
A resting heart rate lower than 60 might also be the outcome of taking certain medications. “Many medications individuals take specifically medication for blood pressure, such as the beta blockers, will lower your heart rate,” Bauman said.
If combined with symptoms, a low heart rate might signify an issue.
“A low heart rate in somebody who is having dizziness and lightheadedness might suggest that they have an abnormality that has to be taken a look at,” Bauman said.
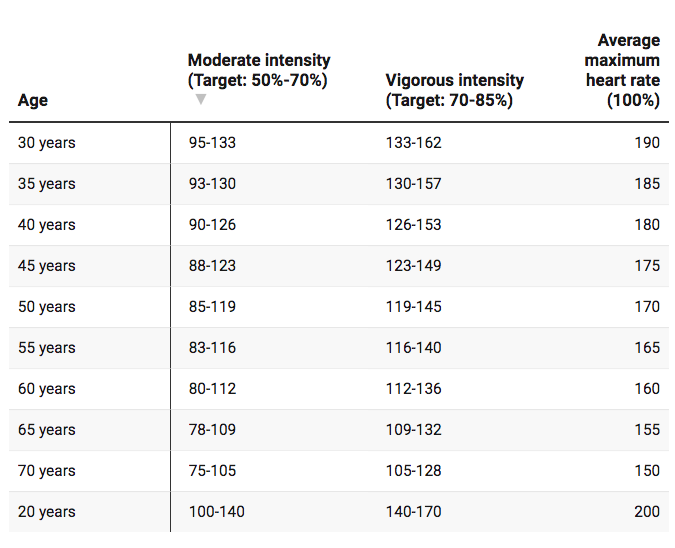
Maximum and target heart rate for people below 50
There is no definitive medical recommendations on when a resting heart rate is high, however a lot of medical specialists concur that a constant heart rate in the upper levels can put too much stress on the heart and other organs. If an individual has a high heart rate at rest and is experiencing other symptoms, doctors might analyze his or her heart function, Bauman said.
Knowing your heart rate during workout sessions can help understand whether you are doing too much or not enough, the AHA says. When individuals work out in their “target heart zone,” they acquire the most benefits and improve their heart’s health. When your heart rate remains in the target zone you know “you are pressing the muscle to obtain more powerful,” Bauman said.
An individual’s target heart rate zone is between 50 and 85 percent of his or her maximum heart rate, according to the AHA.
A lot of commonly, maximum heart rate is calculate by subtracting your age from 220:
220 – Age. For a 30-year-old person, for example: 220 – 30 = 190.
The target zone for a 30-year-old individual would be between 50 and 85 percent of his/her maximum heart rate:
- 50 level: 190 x 0.50 = 95 bpm
- 85 percent level: 190 x 0.85 = 162 bpm
Maximum Heart Rate for People Older than 50
The formula for maximum heart rate works well for people under 40 but for older people it may overestimate their maximum heart rate, Bauman said. For older people, a much better formula for the optimal heart rate is:

208 – (0.75 x Age)
- You can either manually compute your heart rate during exercise or use heart rate displays that wrap around the chest, or are consisted of in sports watches.
- Nevertheless, that’s not to say that working out without getting the heart rate up to the target zone has no advantage, Bauman said.
Apple mojave 10.14 download. ” So many individuals just aren’t doing any workout that I worry less about them reaching their target heart rate and more about them getting out and moving their body,” Bauman said.
Reducing a fast heart rate.
Pulse rates can spike due to anxiety, stress, dehydration and overexertion. Taking a seat and taking sluggish, deep breaths can normally decrease your heart rate. Working out and getting trimmer will usually reduce heart rate, too.
Arrhythmia, tachycardia and other conditions
A variety of conditions can influence your heart rate. An arrhythmia causes the heart to beat too quickly, too sluggish or with an irregular rhythm.
Tachycardia is usually considered to be a resting heart rate of over 100 beats per minute, according to the National Institutes of Health, and typically caused when electrical signals in the heart’s upper chambers fire abnormally. If the heart rate is closer to 150 bpm or higher, it is a condition called supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). In SVT, your heart’s electrical system, which controls the heart rate, is out of whack. This normally needs medical attention.
Bradycardia is a condition where the heart rate is too low, usually less than 60 bpm. This can be the result of problems with the sinoatrial node, which acts as the pacemaker, or damage to the heart as an outcome of a heart attack or heart disease.
High blood pressure vs. high heart rate

Some individuals confuse high blood pressure with a high heart rate. Blood pressure is the measurement of the force of the blood against the walls of arteries, while pulse rate is the number of times your heart beats per minute.
There is no direct connection in between the two, and high blood pressure does not always lead to a high pulse rate, and vice versa. Heart rate goes up during laborious activity, however a vigorous workout may just modestly enhance high blood pressure.
The heart's electrical system
The atria and ventricles work together, alternately contracting and relaxing to pump blood through your heart. The electrical system of your heart is the power source that makes this possible.
Your heartbeat is triggered by electrical impulses that travel down a special pathway through your heart:
- SA node (sinoatrial node) – known as the heart’s natural pacemaker. The impulse starts in a small bundle of specialized cells located in the right atrium, called the SA node. The electrical activity spreads through the walls of the atria and causes them to contract. This forces blood into the ventricles. The SA node sets the rate and rhythm of your heartbeat. Normal heart rhythm is often called normal sinus rhythm because the SA (sinus) node fires regularly.
- AV node (atrioventricular node). The AV node is a cluster of cells in the center of the heart between the atria and ventricles, and acts like a gate that slows the electrical signal before it enters the ventricles. This delay gives the atria time to contract before the ventricles do.
- His-Purkinje Network. This pathway of fibers sends the impulse to the muscular walls of the ventricles and causes them to contract. This forces blood out of the heart to the lungs and body.
- The SA node fires another impulse and the cycle begins again.
At rest, a normal heart beats around 50 to 99 times a minute. Exercise, emotions, fever and some medications can cause your heart to beat faster, sometimes to well over 100 beats per minute.
How fast does the normal heart beat?
How fast the heart beats depends on the body's need for oxygen-rich blood. At rest, the SA node causes your heart to beat about 50 to 100 times each minute. During activity or excitement, your body needs more oxygen-rich blood; the heart rate rises to well over 100 beats per minute.
Medications and some medical conditions may affect how fast your heart-rate is at rest and with exercise.
How do you know how fast your heart is beating?
You can tell how fast your heart is beating (your heart rate) by feeling your pulse. Your heart-rate is the amount of times your heart beats in one minute.
You will need a watch with a second hand.
Place your index and middle finger of your hand on the inner wrist of the other arm, just below the base of the thumb.
You should feel a tapping or pulsing against your fingers. Spss for mac catalina free.
Count the number of taps you feel in 10 seconds.
Multiply that number by 6 to find out your heart-rate for one minute:
Pulse in 10 seconds x 6 = __ beats per minute (your heart-rate)
When feeling your pulse, you can also tell if your heart rhythm is regular or not.
Normal Heart Beat
1. The SA node sets the rate and rhythm of your heartbeat.
2. The SA node fires an impulse. The impulse spreads through the walls of the right and left atria, causing them to contract. This forces blood into the ventricles.
3. The impulse travels to the AV node. Here, the impulse slows for a moment before going on to the ventricles.
Normal Heart Beat Range For Adults
4. The impulse travels through a pathway of fibers called the HIS-Purkinje network. This network sends the impulse into the ventricles and causes them to contract. This forces blood out of the heart to the lungs and body.
Normal Heart Beats A Minute
5. The SA node fires another impulse. The cycle begins again.
